LAUREL, Md. — It’s the plot level for multiple Hollywood blockbuster: A rogue asteroid is hurtling towards Earth, threatening tsunamis, mass destruction and the dying of each human being on the planet.
Humanity has one shot to save lots of itself with courageous, self-sacrificing heroes piloting a spacecraft into the photo voltaic system to destroy the asteroid.
However that’s the films. On Monday night, NASA confirmed what the fact could be like.
There was an asteroid, but it surely wasn’t threatening the Earth. And there was a spacecraft, relying solely on refined know-how. The human heroes of the mission have been truly at a physics and engineering lab between Baltimore and Washington, D.C.
And there was a collision. On this case it was the ultimate act of the Double Asteroid Redirection Take a look at, or DART, a spacecraft that launched in November after which raced across the solar for 10 months because it pursued its goal — a small house rock, Dimorphos, seven million miles from Earth.
“For the primary time, humanity has demonstrated the flexibility to autonomously goal and alter the orbit of a celestial object,” Ralph Semmel, director of the Johns Hopkins College Utilized Physics Laboratory, mentioned throughout a information convention after the crash. The laboratory managed the mission for NASA.
Hitting an asteroid with a high-speed projectile nudges its orbit. For an asteroid headed towards Earth, that could possibly be sufficient to alter a direct hit to a close to miss.
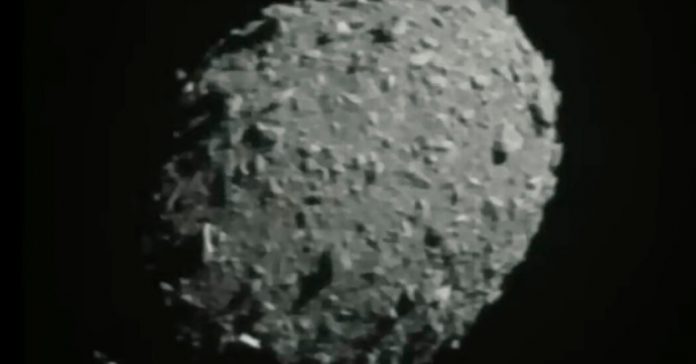
In its final moments, the spacecraft despatched again a sequence of images of the asteroid, Dimorphos, because it approached at greater than 14,000 miles per hour.
DART had noticed Dimorphos solely about an hour earlier, as a dot of sunshine. Then, the pile of celestial rubble grew greater and larger, till the image of the asteroid’s floor strewn with boulders crammed the display. The mission’s engineers have been on their ft, cheering.
“Usually, dropping sign from the spacecraft is a really unhealthy factor,” Dr. Semmel mentioned. “However on this case, it was the perfect end result.”
There was yet another partial picture, however the knowledge by no means made it again to Earth. DART had smashed into the asteroid.
“Wow, that was wonderful, wasn’t it?” mentioned Nancy Chabot, a planetary scientist on the laboratory who works on the mission, throughout the NASA webcast.
With films like “Armageddon,” “Deep Influence” and, extra not too long ago, “Don’t Look Up,” Hollywood has lengthy been fascinated with the prospect of catastrophe raining down from the cosmos. In recent times, scientists and policymakers have additionally taken the risk extra critically than they as soon as did.
For a few years, policymakers lacked urgency to finance efforts to guard the planet from asteroids. However that started to shift partially as a result of astronomers have been capable of finding the entire large asteroids that may wreak planet-wide destruction, just like the one which doomed the dinosaurs 66 million years in the past, mentioned Thomas Statler, this system scientist on the DART mission.
Impacts of a worldwide scale happen very hardly ever, as soon as each 10 million years or so. However now that that risk has been dominated out, planners at NASA and elsewhere commit their consideration to smaller objects in house. These are much more quite a few, and, though they might not set off mass extinctions, they’ll unleash extra vitality than a nuclear bomb.
“The dialog has matured in a very applicable manner,” Dr. Statler mentioned.
The rising concentrate on planetary protection could be in seen in a lot of initiatives that NASA and Congressional appropriators have sponsored. One is the Vera Rubin Observatory, a brand new telescope in Chile that’s financed by america and can systematically scan the night time sky and discover hundreds of probably hazardous asteroids. One other is the NEO Surveyor, a space-based telescope that NASA is working to construct. It too will discover many hazardous asteroids, together with some which can be onerous to identify from Earth.
If any of these asteroids change into on a collision course with Earth, the DART mission reveals that deflecting them is a sensible risk.
For the engineers on the mission, operated by the Johns Hopkins College Utilized Physics Laboratory, the influence, at 7:14 p.m. Japanese time, marked the tip of their work. The spacecraft, working autonomously for the final 4 hours of its existence, efficiently locked on Dimorphos.
That’s much more spectacular as a result of DART’s digital camera noticed Dimorphos for the primary time a bit of greater than an hour earlier than influence. Dimorphos orbits a bigger asteroid, Didymos, and till then, the smaller asteroid was misplaced within the glare of the bigger object. DART’s navigation system then shifted its gaze towards the smaller asteroid.
Up till 5 minutes earlier than influence, mission controllers might have intervened if one thing had gone improper. However they didn’t need to make any changes.
Over the last 5 minutes, the folks within the management room have been spectators, too, like everybody watching the stream of images of Dimorphos. After which it was over. Preliminary evaluation indicated that the spacecraft hit inside about 50 ft of the goal middle.
“I positively really feel relieved,” mentioned Elena Adams, the mission programs engineer. “And it’s completely great to do one thing this wonderful. And we’re so excited to be achieved.”
For asteroid scientists, their work is simply starting.
By design, the crash occurred when the asteroids have been pretty near Earth.
That allowed telescopes on Earth to get a very good look. About 40 of them have been pointed at Didymos and Dimorphos, in line with NASA and the mission’s managers. So have been the Hubble and James Webb house telescopes as was the digital camera on Lucy, one other NASA spacecraft. The LICIACube, a spacecraft in regards to the dimension of a shoe field constructed by the Italian Area Company, trailed DART to take images of the influence and the plume of particles. Its trajectory was shifted to the facet in order that it didn’t additionally crash into the asteroid.
“There’s the remainder of us which can be actually eagerly anticipating the impacts in order that we will take our science and run with it,” mentioned Cristina Thomas, a professor of astronomy and planetary science at Northern Arizona College and lead of the observations working group for the mission. “It’s going to be so nice and such an thrilling once-in-a-lifetime occasion that we’re throwing all the pieces that we have now at it.”
Over the approaching days and weeks, Dr. Thomas and different astronomers can be sifting by means of the info and the photographs to determine what DART did to Dimorphos. The important thing measurement can be how a lot the smaller asteroid, which had been orbiting Didymos each 11 hours and 55 minutes, has sped up. That may mirror how a lot momentum the spacecraft imparted to the asteroid, inflicting it to maneuver nearer to Didymos. The change is predicted to be about 1 p.c, or about seven minutes.
The influence might have given Dimorphos a good greater push if the house rock was a loosely held collectively pile of rubble. The crash of DART would have created a deep crater and despatched a bathe of particles flying into house. That cascade of fabric would have acted just like the thrust of a rocket engine pushing in opposition to the asteroid.
Astronomers need to see if there’s a brightening of the Didymos-Dimorphos system from daylight reflecting off the particles plume. Analyzing the precise colours of sunshine might reveal particulars in regards to the composition of Dimorphos.
Extra detailed research will come years later when Hera, a spacecraft being constructed by the European Area Company, arrives to take a detailed have a look at the 2 asteroids, particularly the scar made by DART. Scientists estimate that there needs to be a crater 30 ft to 60 ft huge.
The asteroid pair takes two years to go across the solar, and a part of the orbit crosses Earth’s. However there isn’t any hazard of both asteroid hitting Earth anytime quickly, and the influence had no probability of knocking it into Earth’s path.
Nonetheless, with a profitable demonstration that an asteroid could be deflected, “I believe that earthlings ought to sleep higher,” Dr. Adams mentioned. “Undoubtedly I’ll.”